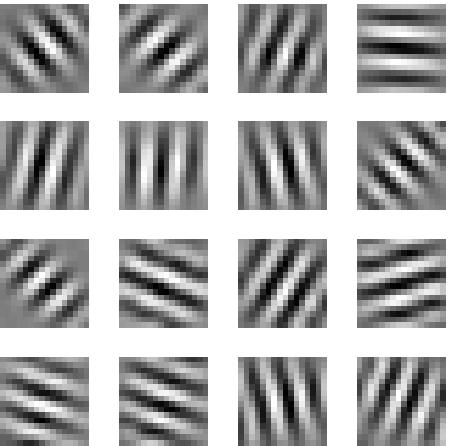
| Matlab source code for the temporal slowness model of complex cells |
Update (24.7.2007)
I fixed a small bug in theshow_optimal.m function, which
caused some of the wavelets shown in the optimal inhibitory stimuli
figure to actually be optimal excitatory stimuli. Many thanks to Saskia
Helbling for pointing that out!
Introduction
This package contains a user-friendly version of the Matlab source code of the model of self-organization of receptive fields based on temporal slowness described in (Berkes and Wiskott 2002, 2003, 2005).The Matlab code includes the functions necessary to create image sequences out of static images, to run a SFA simulation, and to compute the optimal stimuli of the resulting units. The functions are fully customizable such that it is possible to experiment with different parameters settings. A demo script is available to run a default simulation.
This program has been written by Pietro Berkes.
Download and Installation
To use this package you need the sfa-tk v.1.0.1 library.The program has been tested on Matlab 7.0.0.19901 (R14).
.tgz (ca. 1.5 Mb): slowness_model.tgz
To install it, simply unpack the archive into your favorite Matlab
directory. This is going to create a slowness_model
directory. Before you begin to use the functions, make sure that the
sfa_tk/sfa and the sfa_tk/lcov directories
of the sfa-tk library are in your Matlab path.
Online documentation generated with m2html is available here.
Quick start
The script start.m runs a simulation with default settings
and displays the optimal stimuli of the resulting functions. You might
want to edit it in order to change some of the parameters. It takes
on my machine approximately 45 minutes to complete the script.
Contact
If you find a bug or have any kind of feedback please contact
me at  .
.
References
[1] Berkes, P. and Wiskott, L. (2002). Applying Slow Feature Analysis to Image Sequences Yields a Rich Repertoire of Complex Cell Properties. in Artificial Neural Networks - ICANN 2002, ed. José R. Dorronsoro, Springer Verlag, pp. 81-86.
[2] Berkes, P. and Wiskott, L. (2003). Slow feature analysis yields a rich repertoire of complex-cell properties. Cognitive Sciences EPrint Archive (CogPrint) 2804.
[3] Berkes, P. and Wiskott, L. (2005). Slow feature analysis yields a rich repertoire of complex cell properties. Journal of Vision, 5(6), 579-602.